Java日志
java⽇志体系
一、体系概述
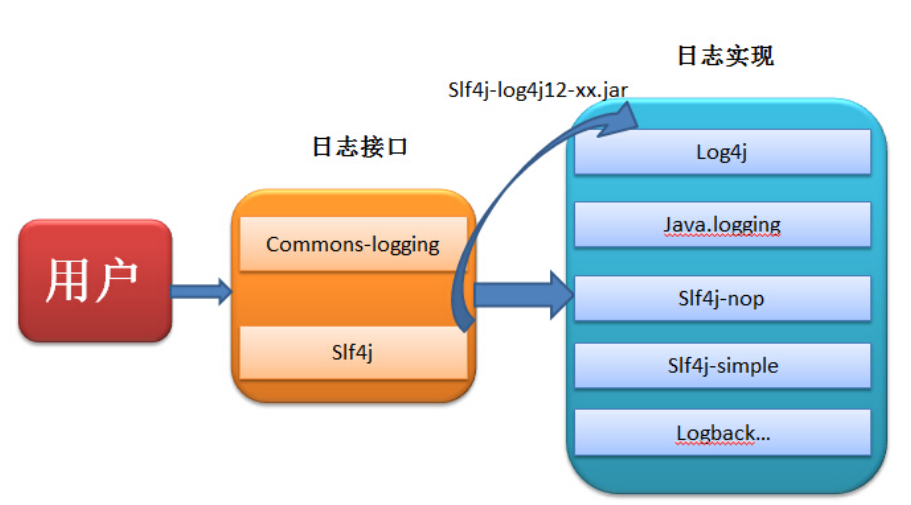
1.1 ⽇志接⼝
- JCL:Apache基⾦会所属的项⽬,是⼀套Java⽇志接⼝,之前叫Jakarta Commons Logging,后更名为Commons Logging,简称JCL
- SLF4J:Simple Logging Facade for Java,缩写Slf4j,是⼀套简易Java⽇志⻔⾯,只提供相关接⼝,和其他⽇志⼯具之间需要桥接
1.2 ⽇志实现
- JUL:JDK中的⽇志⼯具,也称为jdklog、jdk-logging,⾃Java1.4以来sun的官⽅提供。
- Log4j:⾪属于Apache基⾦会的⼀套⽇志框架,现已不再维护
- Log4j2:Log4j的升级版本,与Log4j变化很⼤,不兼容
- Logback:⼀个具体的⽇志实现框架,和Slf4j是同⼀个作者,性能很好
二、日志配置
2.1 概述
1)⽇志级别:编码最经常⽤到的主流分级如下(由低到⾼):
- trace:路径跟踪
- debug:⼀般⽤于⽇常调式
- info:打印重要信息
- warn:给出警告
- error:出现错误或问题
2)⽇志组件
- appender:⽇志输出⽬的地,负责⽇志的输出 (输出到什么 地⽅)
- logger:⽇志记录器,负责收集处理⽇志记录 (如何处理⽇志)
- layout:⽇志格式化,负责对输出的⽇志格式化(以什么形式展现)
2.2 logback
http://logback.qos.ch/manual/index.html
1)配置⽂件:
- Logback tries to find a file called logback-test.xml in the classpath.
- If no such file is found, logback tries to find a file called logback.groovy in the classpath.
- If no such file is found, it checks for the file logback.xml in the classpath..
- If no such file is found, service-provider loading facility (introduced in JDK 1.6) is used to resolve the implementation of com.qos.logback.classic.spi.Configurator interface by looking up the file META-INF\services\ch.qos.logback.classic.spi.Configurator in the class path. Its contents should specify the fully qualified class name of the desired Configurator implementation.
- If none of the above succeeds, logback configures itself automatically using the BasicConfigurator which will cause logging output to be directed to the console.
2)级别:
- ⽇志打印级别 ALL > TRACE > FATAL > DEBUG > INFO > WARN > ERROR > OFF
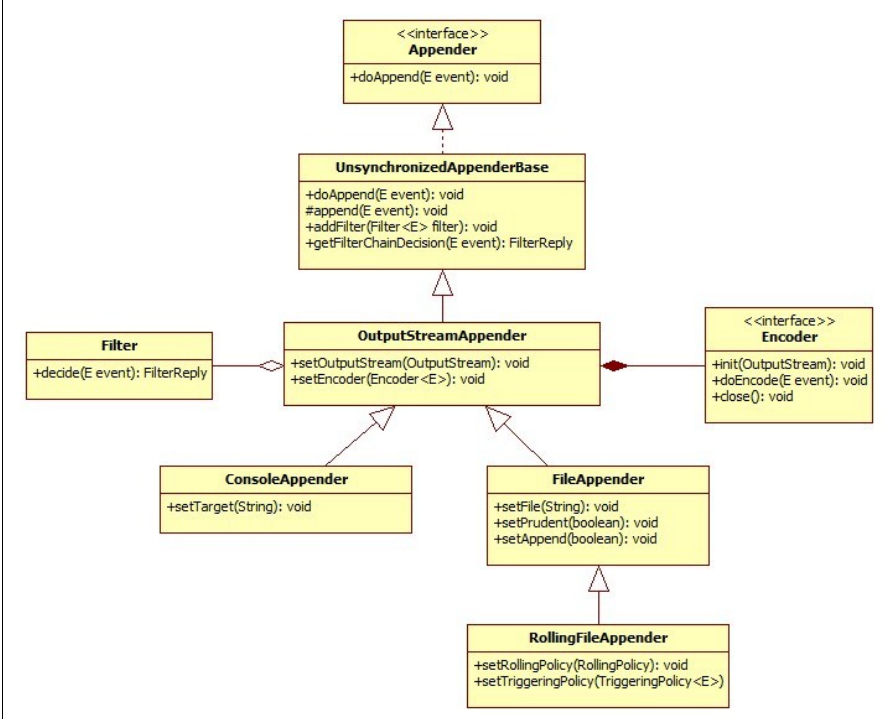
3)处理器:
http://logback.qos.ch/manual/appenders.html
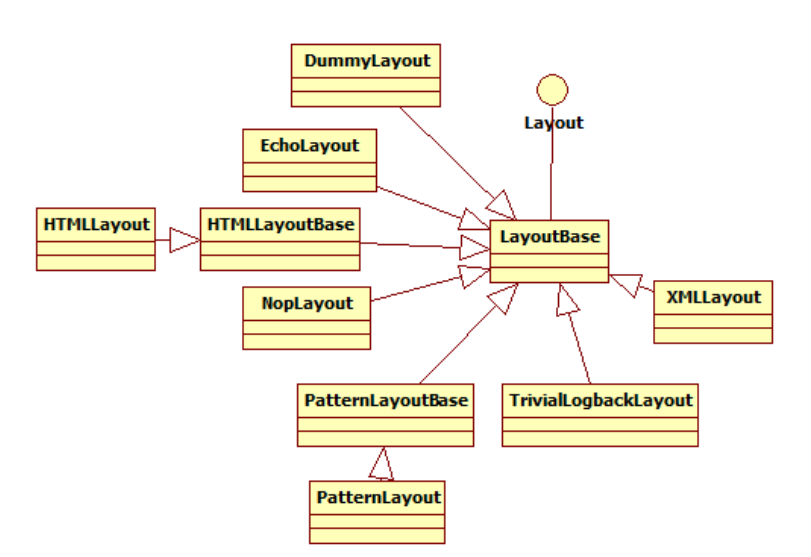
4)格式化:
http://logback.qos.ch/manual/layouts.html
\5) 代码实战:
- Appender:Console,Rollingfile
- Layout:Xml,Pattern,Html , ⾃定义
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration scan="true" scanPeriod="3 seconds" debug="false">
<!-- lOGGER PATTERN 根据个⼈喜好选择匹配 -->
<property name="logPattern" value="logback:[ %-5level] [%date{yyyy-MM-dd
HH:mm:ss.SSS}] %logger{96} [%line] [%thread]- %msg%n"></property>
<!-- 动态⽇志级别 -->
<jmxConfigurator/>
<!-- 控制台的标准输出 -->
<appender name="STDOUT" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder>
<charset>UTF-8</charset>
<pattern>${logPattern}</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<!-- 滚动⽂件 -->
<appender name="ROLLING_FILE"
class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<filter class="ch.qos.logback.classic.filter.LevelFilter">
<level>DEBUG</level>
<onMatch>ACCEPT</onMatch>
<onMismatch>DENY</onMismatch>
</filter>
<file>./logback.log</file>
<rollingPolicy
class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<fileNamePattern>./logback.log.%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.zip</fileNamePattern>
<!-- 最⼤保存时间 -->
<maxHistory>2</maxHistory>
</rollingPolicy>
<encoder>
<pattern>${logPattern}</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<!-- DB -->
<appender name="DB" class="ch.qos.logback.classic.db.DBAppender">
<connectionSource
class="ch.qos.logback.core.db.DriverManagerConnectionSource">
<driverClass>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</driverClass>
<url>jdbc:mysql://172.17.0.203:3306/log?useSSL=false</url>
<user>root</user>
<password>root</password>
</connectionSource>
</appender>
<!-- ASYNC_LOG -->
<appender name="ASYNC_LOG" class="ch.qos.logback.classic.AsyncAppender">
<!-- 不丢失⽇志.默认的,如果队列的80%已满,则会丢弃TRACT、DEBUG、INFO级别的⽇志 -->
<discardingThreshold>0</discardingThreshold>
<!-- 更改默认的队列的深度,该值会影响性能.默认值为256 -->
<queueSize>3</queueSize>
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT"/>
</appender>
<appender name="STDOUT" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder class="ch.qos.logback.core.encoder.LayoutWrappingEncoder">
<!--<charset>UTF-8</charset>-->
<!--<pattern>${logPattern}</pattern>-->
<!--<layout class="com.itheima.logback.MySampleLayout" />-->
<layout class="ch.qos.logback.classic.html.HTMLLayout">
<pattern>%relative%thread%mdc%level%logger%msg</pattern>
</layout>
<!--<layout class="ch.qos.logback.classic.log4j.XMLLayout">-->
<!--<locationInfo>false</locationInfo>-->
<!--</layout>-->
</encoder>
</appender>
<!-- ⽇志的记录级别 -->
<!-- 在定义后引⽤APPENDER -->
<root level="DEBUG">
<!-- 控制台 -->
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT"/>
<!-- ROLLING_FILE -->
<appender-ref ref="ROLLING_FILE"/>
<!-- ASYNC_LOG -->
<appender-ref ref="ASYNC_LOG"/>
</root>
</configuration>
2.3 log4j2
1)配置⽂件:
- Log4j will inspect the log4j.configurationFile system property and, if set, will attempt to
- load the configuration using the ConfigurationFactory that matches the file extension.
- If no system property is set the YAML ConfigurationFactory will look for log4j2-test.yaml
- or log4j2-test.yml in the classpath.
- If no such file is found the JSON ConfigurationFactory will look for log4j2-test.json or
- log4j2-test.jsn in the classpath.
- If no such file is found the XML ConfigurationFactory will look for log4j2-test.xml in the
- classpath.
- If a test file cannot be located the YAML ConfigurationFactory will look for log4j2.yaml or
- log4j2.yml on the classpath.
- If a YAML file cannot be located the JSON ConfigurationFactory will look for log4j2.json or
- log4j2.jsn on the classpath.
- If a JSON file cannot be located the XML ConfigurationFactory will try to locate log4j2.xml
- on the classpath.
- If no configuration file could be located the DefaultConfiguration will be used. This will
- cause logging output to go to the console.
2)级别:
- 从低到⾼为:ALL < TRACE < DEBUG < INFO < WARN < ERROR < FATAL < OFF
3)处理器:
http://logging.apache.org/log4j/2.x/manual/appenders.html
- FileAppender 普通地输出到本地⽂件
- KafkaAppender 输出到kafka队列
- FlumeAppender 将⼏个不同源的⽇志汇集、集中到⼀处。
- JMSQueueAppender,JMSTopicAppender 与JMS相关的⽇志输出
- RewriteAppender 对⽇志事件进⾏掩码或注⼊信息
- RollingFileAppender 对⽇志⽂件进⾏封存(详细)
- RoutingAppender 在输出地之间进⾏筛选路由
- SMTPAppender 将LogEvent发送到指定邮件列表
- SocketAppender 将LogEvent以普通格式发送到远程主机
- SyslogAppender 将LogEvent以RFC 5424格式发送到远程主机
- AsynchAppender 将⼀个LogEvent异步地写⼊多个不同输出地
- ConsoleAppender 将LogEvent输出到命令⾏
- FailoverAppender 维护⼀个队列,系统将尝试向队列中的Appender依次输出LogEvent,直到有⼀个成功为⽌
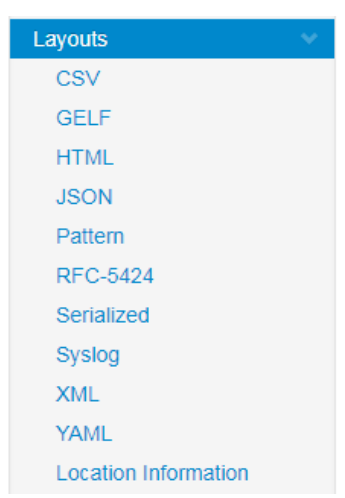
4)格式化:
http://logging.apache.org/log4j/2.x/manual/layouts.html
5)代码实战:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!--⽇志级别以及优先级排序: OFF > FATAL > ERROR > WARN > INFO > DEBUG > TRACE >
ALL -->
<!--status="WARN" :⽤于设置log4j2⾃身内部⽇志的信息输出级别,默认是OFF-->
<!--monitorInterval="30" :间隔秒数,⾃动检测配置⽂件的变更和重新配置本身-->
<configuration status="info" monitorInterval="30">
<Properties>
<!--⾃定义⼀些常量,之后使⽤${变量名}引⽤-->
<Property name="pattern">log4j2:[%-5p]:%d{YYYY-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} [%t]
%c{1}:%L - %msg%n</Property>
</Properties>
<!--appenders:定义输出内容,输出格式,输出⽅式,⽇志保存策略等,常⽤其下三种标签
[console,File,RollingFile]-->
<appenders>
<!--console :控制台输出的配置-->
<Console name="Console" target="SYSTEM_OUT">
<PatternLayout pattern="${pattern}"/>
</Console>
<!--File :同步输出⽇志到本地⽂件-->
<!--append="false" :根据其下⽇志策略,每次清空⽂件重新输⼊⽇志,可⽤于测试-->
<File name="File" fileName="./log4j2-file.log" append="false">
<PatternLayout pattern="${pattern}"/>
</File>
<RollingFile name="RollingFile" fileName="./log4j2-rollingfile.log"
filePattern="./$${date:yyyy-MM}/log4j2-%d{yyyy-MM-dd}-
%i.log">
<!--ThresholdFilter :⽇志输出过滤-->
<!--level="info" :⽇志级别,onMatch="ACCEPT" :级别在info之上则接
受,onMismatch="DENY" :级别在info之下则拒绝-->
<ThresholdFilter level="debug" onMatch="ACCEPT" onMismatch="DENY"/>
<PatternLayout pattern="${pattern}"/>
<!-- Policies :⽇志滚动策略-->
<Policies>
<!-- TimeBasedTriggeringPolicy :时间滚动策略,
默认0点产⽣新的⽂件,
interval="6" : ⾃定义⽂件滚动时间间隔,每隔6⼩时产⽣新⽂件,
modulate="true" : 产⽣⽂件是否以0点偏移时间,即6点,12点,18点,0点-->
<TimeBasedTriggeringPolicy interval="6" modulate="true"/>
<!-- SizeBasedTriggeringPolicy :⽂件⼤⼩滚动策略-->
<SizeBasedTriggeringPolicy size="1 MB"/>
</Policies>
<!-- DefaultRolloverStrategy属性如不设置,则默认为最多同⼀⽂件夹下7个⽂
件,这⾥设置了20 -->
<DefaultRolloverStrategy max="20"/>
</RollingFile>
</appenders>
<!--然后定义logger,只有定义了logger并引⼊的appender,appender才会⽣效-->
<loggers>
<!--过滤掉spring和mybatis的⼀些⽆⽤的DEBUG信息-->
<!--Logger节点⽤来单独指定⽇志的形式,name为包路径,⽐如要为org.springframework
包下所有⽇志指定为INFO级别等。 -->
<logger name="org.springframework" level="INFO"></logger>
<logger name="org.mybatis" level="INFO"></logger>
<!--AsyncLogger :异步⽇志,LOG4J有三种⽇志模式,全异步⽇志,混合模式,同步⽇志,性能
从⾼到底,线程越多效率越⾼,也可以避免⽇志卡死线程情况发⽣-->
<!--additivity="false" : additivity设置事件是否在root logger输出,为了避免重
复输出,可以在Logger 标签下设置additivity为”false”-->
<AsyncLogger name="AsyncLogger" level="trace" includeLocation="true"
additivity="true">
<appender-ref ref="Console"/>
</AsyncLogger>
<logger name="Kafka" additivity="false" level="debug">
<appender-ref ref="Kafka"/>
<appender-ref ref="Console"/>
</logger>
<!-- Root节点⽤来指定项⽬的根⽇志,如果没有单独指定Logger,那么就会默认使⽤该Root
⽇志输出 -->
<root level="info">
<appender-ref ref="Console"/>
<!--<appender-ref ref="File"/>-->
<!--<appender-ref ref="RollingFile"/>-->
<!--<appender-ref ref="Kafka"/>-->
</root>
</loggers>
</configuration>
2.4 slf4j
1)配置⽂件:
** 具体⽇志输出内容取决于⽣效的具体⽇志实现**
2)级别:
** slf4j⽇志级别有五种:ERROR、WARN、INFO、DEBUG、TRACE,级别从⾼到底**
3)slf⽇志实现:
<!--slf转其他⽇志-->
<!--slf - jcl-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-jcl</artifactId>
<version>1.7.30</version>
</dependency>
<!-- slf - log4j -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
<version>1.7.30</version>
</dependency>
<!-- slf4j - log4j2 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-slf4j-impl</artifactId>
<version>2.13.0</version>
</dependency>
<!--slf - jul-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-jdk14</artifactId>
<version>1.7.30</version>
</dependency>
<!--slf - simplelog-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-simple</artifactId>
<version>1.7.30</version>
</dependency>
<!--slf - logback-->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-core</artifactId>
<version>1.2.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.2.3</version>
</dependency>
问题:多个桥接器的话,slf4j怎么处理呢?
** 使⽤在class path中较早出现的那个,如在maven中,会使⽤在pom.xml中定义较靠前的桥接器**
** ⼩知识:桥接器会传递依赖到对应的下游⽇志组件,⽐如slf4j-log4j12会附带log4j的jar包依赖(代码验证)**
4)其他⽇志转slf
<!--其他⽇志转slf-->
<!--jul - slf-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>jul-to-slf4j</artifactId>
<version>1.7.30</version>
</dependency>
<!--jcl - slf-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>jcl-over-slf4j</artifactId>
<version>1.7.30</version>
</dependency>
<!--log4j - slf-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-over-slf4j</artifactId>
<version>1.7.30</version>
</dependency>
<!--log4j2 - slf-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-to-slf4j</artifactId>
<version>2.13.0</version>
</dependency>
三、使用建议
3.1 ⻔⾯约束
** 使⽤⻔⾯,⽽不是具体实现**

3.2 依赖约束
** ⽇志实现坐标应该设置为optional并使⽤runtime scope**
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-core</artifactId>
<version>${log4j.version}</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-slf4j-impl</artifactId>
<version>${log4j.version}</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
** 设为optional,依赖不会传递,这样如果你是个lib项⽬,然后别的项⽬使⽤了你这个lib,不会被引⼊不想要的Log Implementation 依赖;**
Scope设置为runtime,是为了防⽌开发⼈员在项⽬中直接使⽤Log Implementation中的类,强制约束开发⼈员使⽤Facade接⼝。
3.3 避免传递
** **尽量⽤exclusion排除依赖的第三⽅库中的⽇志坐标
实例:依赖jstorm会引⼊Logback和log4j-over-slf4j,如果你在⾃⼰的项⽬中使⽤Log4j或其他Log实现的话,就需要加上exclusion:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.jstorm</groupId>
<artifactId>jstorm-core</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-over-slf4j</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
3.4 注意写法
避免为不会输出的log买单
logger.debug("this is debug: " + message);
logger.debug("this is json msg: {}", toJson(message));
即使⽇志级别⾼于debug不会打印,依然会做字符串连接操作;
第⼆条虽然⽤了SLF4J/Log4j2 中的懒求值⽅式,但是toJson()这个函数却是总会被调⽤并且开销更⼤。
推荐的写法如下:
// SLF4J/LOG4J2
logger.debug("this is debug:{}", message);
// LOG4J2
logger.debug("this is json msg: {}", () -> toJson(message));
// SLF4J/LOG4J2
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("this is debug: " + message);
}
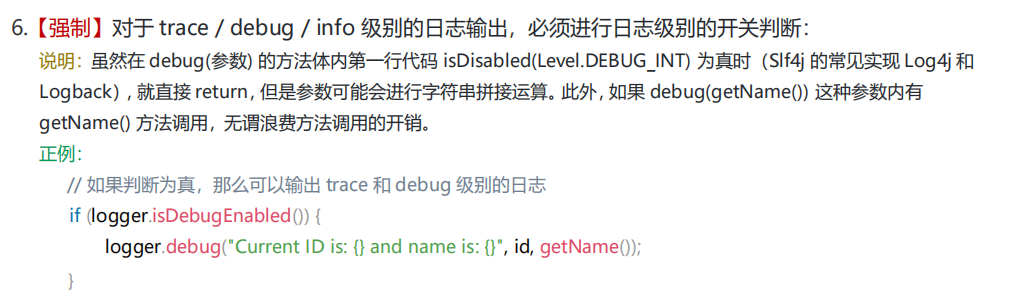
3.5** 减少分**
** **输出的⽇志中尽量不要使⽤⾏号,函数名等信息
** 原因是,为了获取语句所在的函数名,或者⾏号,log库的实现都是获取当前的stacktrace,然后分**
**析取出这些信息,⽽**获取stacktrace的代价是很昂贵的。如果有很多的⽇志输出,就会占⽤⼤量的
CPU。在没有特殊需要的情况下,建议不要在⽇志中输出这些这些字段。
3.6 精简⾄上
** **log中尽量不要输出稀奇古怪的字符,这是个习惯和约束问题。有的同学习惯⽤这种语句:
logger.debug("=====================================:{}",message);
** 输出了⼤量⽆关字符,虽然⾃⼰⼀时痛快,但是如果所有⼈都这样做的话,那log输出就没法看了!**
正确的做法是⽇志只输出必要信息,如果要过滤,后期使⽤grep来筛选,只查⾃⼰关⼼的⽇志。