CompletableFuture的使用
CompletableFuture使用
一、核心API
- public static CompletableFuture runAsync(Runnable runnable)
- public static CompletableFuture runAsync(Runnable runnable,Executor executor)
- public static CompletableFuture supplyAsync(Supplier supplier)
- public static CompletableFuture supplyAsync(Supplier supplier,Executor executor)
没有指定Executor的方法,直接使用默认的ForkJoinPool.commonPool() 作为它的线程池执行异步代码。
如果指定线程池,则使用我们自定义的或者特别指定的线程池执行异步代码
线程池参数设置可以参考
CPU 密集型运算
通常采用 cpu 核数 + 1 能够实现最优的 CPU 利用率,+1 是保证当线程由于页缺失故障(操作系统)或其它原因导致暂停时,额外的这个线程就能顶上去,保证 CPU 时钟周期不被浪费。
I/O 密集型运算
CPU 不总是处于繁忙状态,例如,当你执行业务计算时,这时候会使用 CPU 资源,但当你执行 I/O 操作时、远程RPC 调用时,包括进行数据库操作时,这时候 CPU 就闲下来了,你可以利用多线程提高它的利用率。
经验公式如下
线程数 = 核数 * 期望 CPU 利用率 * 总时间(CPU计算时间+等待时间) / CPU 计算时间。
无返回值 使用
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException
{
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"-----come in");
//暂停几秒钟线程
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("-----task over");
});
System.out.println(future.get());
}
有返回值
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"-----come in");
//暂停几秒钟线程
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("-----task over");
return 1;
});
System.out.println(future.get());
}
二、CompletableFuture常用方法
1、获得结果和触发计算
- public T get() 主线程阻塞的等待返回结果。
- public T get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) 带超时时间主线程阻塞的等待返回结果。
- public T getNow(T valueIfAbsent) 没有计算完成的情况下,返回一个默认结果
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException
{
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
return 1;
});
//计算没有完成,返回0,计算完成,返回计算结果
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(completableFuture.getNow(0));
}
- public T join() 完成后返回结果值
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException
{
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "hello")
.thenApply(r -> r + " world").join());
}
- public boolean complete(T value) 如果尚未完成,将返回的值get()种相关方法为给定值
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException
{
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
return 1;
});
//注释掉暂停线程,get还没有算完只能返回complete方法设置的444;暂停2秒钟线程,异步线程能够计算完成返回get
// try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
//当调用CompletableFuture.get()被阻塞的时候,complete方法就是结束阻塞并get()获取设置的complete里面的值.
System.out.println(completableFuture.complete(0)+"\t"+completableFuture.get());
}
2、对计算结果进行处理
- public boolean thenApply(T value)
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException
{
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 20, 1L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(50), Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
//当一个线程依赖另一个线程时用 thenApply 方法来把这两个线程串行化,
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//暂停几秒钟线程
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println("111");
return 111;
},threadPoolExecutor).thenApply(f -> {
//int age = 10/0; // 异常情况:那步出错就停在那步。
System.out.println("222");
return f + 1;
}).thenApply(f -> {
System.out.println("333");
return f + 1;
}).whenCompleteAsync((v,e) -> {
System.out.println("-----v: "+v);
}).exceptionally(e -> {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
});
threadPoolExecutor.shutdown();
}
- handle
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException
{
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 20, 1L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(50), Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
//当一个线程依赖另一个线程时用 handle 方法来把这两个线程串行化,
// 异常情况:有异常也可以往下一步走,根据带的异常参数可以进一步处理
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//暂停几秒钟线程
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println("111");
return 111;
},threadPoolExecutor).handle((f,e) -> {
int age = 10/0;
System.out.println("222");
return f + 1;
}).handle((f,e) -> {
System.out.println("333");
return f + 1;
}).whenCompleteAsync((v,e) -> {
System.out.println("*****v: "+v);
}).exceptionally(e -> {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
});
threadPoolExecutor.shutdown();
}
whenComplete和whenCompleteAsync的区别:
whenComplete:是执行当前任务的线程执行继续执行whenComplete的任务。
whenCompleteAsync:是执行把whenCompleteAsync这个任务继续提交给线程池来进行执行。
3、对计算结果进行消费
- thenAccept 接收任务的处理结果,并消费处理,无返回结果
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException {
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 1)
.thenApply(f -> f + 2)
.thenApply(f -> f + 3)
.thenApply(f -> f + 4)
.thenAccept(System.out::println);
}
thenRun(Runnable runnable) 任务 A 执行完执行 B,并且 B 不需要 A 的结果
thenAccept(Consumer action) 任务 A 执行完执行 B,B 需要 A 的结果,但是任务 B 无返回值
thenApply(Function fn) 任务 A 执行完执行 B,B 需要 A 的结果,同时任务 B 有返回值
4、对计算速度进行选用
- applyToEither
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException
{
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "---come in ");
//暂停几秒钟线程
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
return 10;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "---come in ");
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
return 20;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> thenCombineResult = completableFuture1.applyToEither(completableFuture2,f -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "---come in ");
return f + 1;
});
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + thenCombineResult.get());
}
5、对计算结果进行合并
- thenCombine(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn)
两个CompletionStage任务都完成后,最终能把两个任务的结果一起交给thenCombine 来处理
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException
{
CompletableFuture<Integer> thenCombineResult = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "---come in 1");
return 10;
}).thenCombine(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "---come in 2");
return 20;
}), (x,y) -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "---come in 3");
return x + y;
}).thenCombine(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "---come in 4");
return 30;
}),(a,b) -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "---come in 5");
return a + b;
});
System.out.println("-----主线程结束,END");
System.out.println(thenCombineResult.get());
}
三、使用实例
下面是java虚拟线程官方视频的一个使用示例,翻译后视频连接【通向Java21-02-Java虚拟线程】 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Ju4y1Q788/?share_source=copy_web&vd_source=36048a8ec755b67c73e0b0233a43f92b
下面代码意思是确保用户已保存在数据库中。 然后取出购物车。然后循环用户选择的商品,计算总价。 然后调用支付服务,并记录交易ID。 通过所有这些信息,发送包含交易所有详细信息的电子邮件
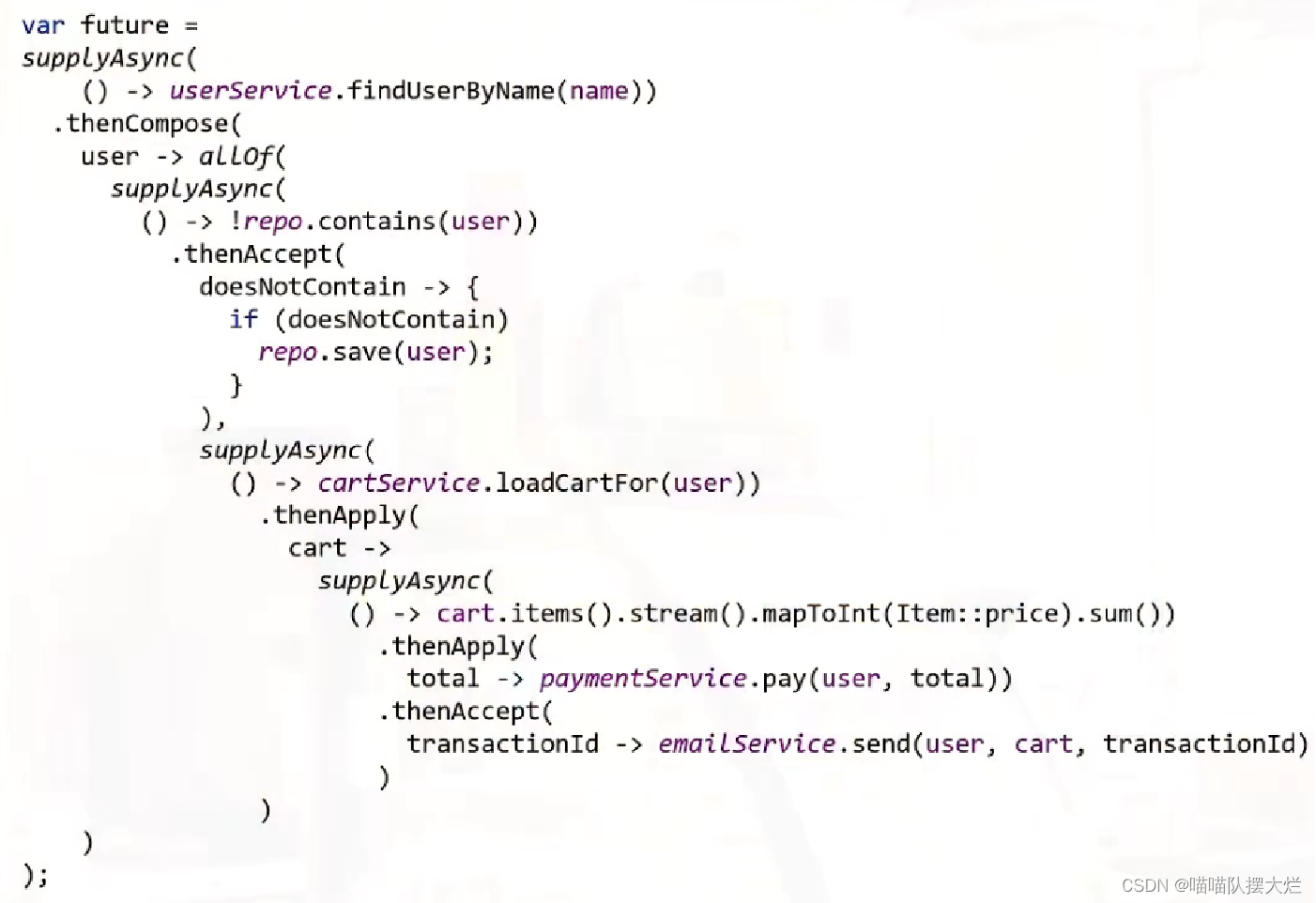
2、使用Completablefutrue获取一组数据的详细信息
List<Object> collect = list.stream().map(v ->
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> userService.getById(v))
).collect(Collectors.toList())
.stream()
.map(CompletableFuture::join)
.collect(Collectors.toList());